|

CLICK ON weeks 0 - 40 and follow along every 2 weeks of fetal development
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
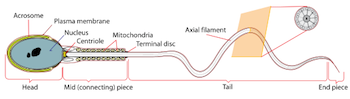
Developmental Biology - Male Infertility Roots of Infertility's In Some Sperm DNA With this information, the team produced a mouse in which serine 56 was substituted for alanine, dephosphomimetic of dephosphorylated serine — a single amino acid replacement. Diagram of human spermatozoa. Wikipedia Itoh's team hopes to continue unravelling the complex network of gene interactions and protein modifications in spermatozoa to find other possible ways of affecting infertility. Protamine dephosphorylation for fertility During the final stage of spermatogenesis, protamines tightly package DNA in the mature sperm. Itoh et al. generated mice deficient in the heat shock protein and chaperone Hspa4l, which is implicated in spermatogenesis. The mice were infertile with malformed sperm heads, a phenotype similar to that of mice deficient in the phosphatase Ppp1cc2. The authors showed that Hspa4l was required to release Ppp1cc2 from a complex with other chaperones, enabling its translocation to chromatin. In vitro studies showed that Ppp1cc2 dephosphorylated protamine 2 at Ser56. Expression of the unphosphorylatable protamine 2 S56A mutant reversed the infertility of Hspa4l-deficient mice, suggesting that the dephosphorylation of protamine 2 at Ser56 is important for its role in sperm maturation. Abstract The posttranslational modification of histones is crucial in spermatogenesis, as in other tissues; however, during spermiogenesis, histones are replaced with protamines, which are critical for the tight packaging of the DNA in sperm cells. Protamines are also posttranslationally modified by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, which prompted our investigation of the underlying mechanisms and biological consequences of their regulation. On the basis of a screen that implicated the heat shock protein Hspa4l in spermatogenesis, we generated mice deficient in Hspa4l (Hspa4l-null mice), which showed male infertility and the malformation of sperm heads. These phenotypes are similar to those of Ppp1cc-deficient mice, and we found that the amount of a testis- and sperm-specific isoform of the Ppp1cc phosphatase (Ppp1cc2) in the chromatin-binding fraction was substantially less in Hspa4l-null spermatozoa than that in those of wild-type mice. We further showed that Ppp1cc2 was a substrate of the chaperones Hsc70 and Hsp70 and that Hspa4l enhanced the release of Ppp1cc2 from these complexes, enabling the freed Ppp1cc2 to localize to chromatin. Pull-down and in vitro phosphatase assays suggested the dephosphorylation of protamine 2 at serine 56 (Prm2 Ser56) by Ppp1cc2. To confirm the biological importance of Prm2 Ser56 dephosphorylation, we mutated Ser56 to alanine in Prm2 (Prm2 S56A). Introduction of this mutation to Hspa4l-null mice (Hspa4l-/-; Prm2S56A/S56A) restored the malformation of sperm heads and the infertility of Hspa4l-/- mice. The dephosphorylation signal to eliminate phosphate was crucial, and these results unveiled the mechanism and biological relevance of the dephosphorylation of Prm2 for sperm maturation in vivo. Authors Katsuhiko Itoh, Gen Kondoh, Hitoshi Miyachi, Manabu Sugai, Yoshiyuki Kaneko, Satsuki Kitano, Hitomi Watanabe, Ryota Maeda, Akihiro Imura, Yu Liu, Chizuru Ito, Shigeyoshi Itohara, Kiyotaka Toshimori, and Jun Fujita. Acknowledgements About Kyoto University Kyoto University is one of Japan and Asia's premier research institutions, founded in 1897 and responsible for producing numerous Nobel laureates and winners of other prestigious international prizes. A broad curriculum across the arts and sciences at both undergraduate and graduate levels is complemented by numerous research centers, as well as facilities and offices around Japan and the world. For more information please see: http://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/en Return to top of page | Mar 27 2019 Fetal Timeline Maternal Timeline News   During mouse spermiogenesis, histones are replaced with protamines, which are critical for tightly packaging DNA into sperm heads. Acrosin can then be released from the acrosome or 'head' of a sperm allowing it to penetrate the Zona Pellucida surrounding an egg and begin fertilization. WILD-TYPE refers to normal mouse sperm. Hspa41-deficient sperm can be overcome with the addition of Protamine 2 at serine 56 (Prm2 Ser56) Image: Kyoto University/Itoh Lab
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||